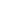Duduk
Friday, May 5, 2023
Duduk or tsiranapogh is a double reed woodwind instrument made of apricot wood originating from Armenia.
Variations of the Armenian duduk appear throughout the Caucasus and the Middle East,including Azerbaijan, Georgia, Russia, Turkey, and Iran. Duduk, Balaban, and Mey are almost identical, except for historical and geographical differences.
It is commonly played in pairs: while the first player plays the melody, the second plays a steady drone called dum, and the sound of the two instruments together creates a richer, more haunting sound. The unflattened reed and cylindrical body produce a sound closer to the English horn than the oboe or bassoon. Unlike other double-reed instruments like the oboe or shawm, the duduk has a very large reed proportional to its size.
The duduk is a double reed instrument with ancient origins, having existed since at least the fifth century, while there are Armenian scholars who believe it existed more than 1,500 years before that. The earliest instruments similar to the duduk's present form are made of bone or entirely of cane. Today, the duduk is exclusively made of wood with a large double reed, with the body made from aged apricot wood.
The particular tuning depends heavily on the region in which it is played. In the twentieth century, the Armenian duduk began to be standardized diatonic in scale and single-octave in range. Accidentals, or chromatics are achieved using fingering techniques. The instrument's body also has different lengths depending upon the range of the instrument and region. The reed (Armenian: եղեգն, eġegn), is made from one or two pieces of cane in a duck-bill type assembly. Unlike other double-reed instruments, the reed is quite wide, helping to give the duduk both its unique, mournful sound, as well as its remarkable breathing requirements. The duduk player is called dudukahar (դուդուկահար) in Armenian.